ZigBee is a wireless communication technology that uses radio frequencies to connect devices and support data exchange. It is widely used in applications such as smart home automation, industrial control systems, and warehouse management due to its low power consumption, scalability, and reliable performance in environments with high levels of interference.
ZigBee’s ability to form large mesh networks enhances its robustness, making it ideal for complex environments. Beyond basic connectivity, ZigBee plays an important role in Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS), enabling the real-time tracking and monitoring of assets, equipment, and individuals using ZigBee End Devices (Tags), ZigBee Routers, and ZigBee Coordinators.
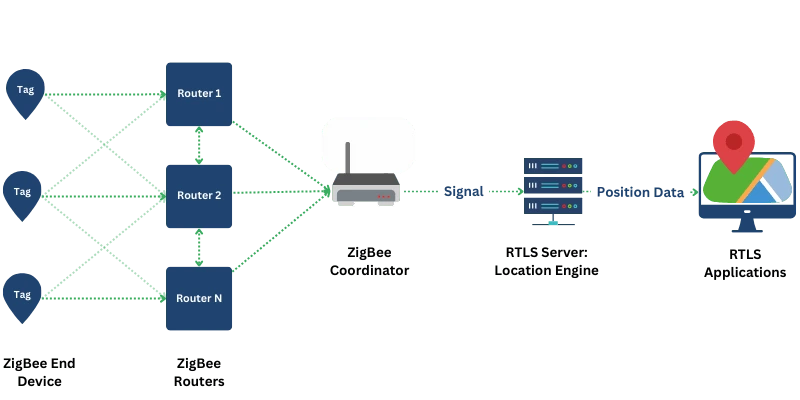
At the core of ZigBee RTLS is its mesh network topology, which allows devices to communicate directly or through intermediary nodes (ZigBee End Devices, ZigBee Routers, and the ZigBee Coordinator).
In a mesh network, each device can transmit data not only to the central ZigBee Coordinator but also to other nodes, enabling data to “hop” from one device to another. This structure increases the system’s reliability because even if one node fails, the data can find an alternate path to its destination. This automatic recovery capability ensures continuous, robust communication, making ZigBee ideal for environments with physical obstacles or signal interference.

ZigBee operates in unlicensed frequency bands, making it globally compatible without the need for special licensing. The common frequency ranges include:
The choice of frequency can affect the range, data rate, and performance depending on the deployment environment.
ZigBee RTLS operates through a combination of wireless communication, mesh networking, and data processing to track and manage the location of assets, people, or equipment in real time. The system relies on the interaction of four key components:
1. ZigBee Coordinator (Master Node):
2. ZigBee Routers (Router Nodes):
3. ZigBee End device (Tags):
4. Data Manager:
ZigBee RTLS determines the precise location of each tag using various positioning techniques that rely on signal properties such as strength, time, and angle. The accuracy of these methods can vary depending on the deployment environment and system configuration. Here are the primary methods used:
1. Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) Based Positioning:
2. Time of Arrival (ToA) Based Positioning:
3. Angle of Arrival (AoA) Based Positioning:
4. Hybrid Positioning Methods:
The range of ZigBee is the maximum distance over which devices can communicate, varying based on indoor or outdoor environments and factors like interference and obstacles.
Indoors: 10–100 meters, depending on building layout and interference.
Outdoors: Up to 300 meters with clear line-of-sight and minimal barriers.
Power Output: Higher output extends range but increases power use.
Obstacles: Walls, metal, and dense materials reduce signal strength.
Interference: Wi-Fi and other devices on similar frequencies can disrupt communication.
Antenna Quality: Better antennas improve range and stability.
Mesh Networking: Allows signals to “hop” between devices, extending coverage.
Energy Efficiency: Supports ultra-low power consumption, enabling tags to operate for months or years on small batteries—ideal for IoT applications.
Robust Mesh Networking: Enhances reliability with self-healing mesh networks, ensuring continuous connectivity even if a node fails.
Scalability: Easily supports hundreds to thousands of devices, making it suitable for large-scale RTLS deployments.
Interoperability: Based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard, ensuring seamless integration with various IoT devices and platforms.
Reliability in Challenging Environments: Performs well in high-interference areas like factories and dense urban settings.
Flexible Frequency Options: Operates on global unlicensed bands (2.4 GHz, 915 MHz, 868 MHz) for versatile deployment.
Cost-Effective Solution: Affordable hardware with low power consumption reduces operational costs over time.
Secure Communication: Features AES-128 encryption to ensure data security across the network.
ZigBee RTLS supports real-time tracking and indoor positioning across various industries:
📍 We’re expanding our horizons! Stay tuned for upcoming product and service launches.📍
©2024 anyRTLS, All rights reserved.